Cryptocurrencies are very volatile assets, with significant price fluctuations compared to the conventional currency. However, specific cryptocurrencies are meant to maintain a consistent price. Cryptocurrencies, known as "stablecoins", are designed to be linked to another cryptocurrency, fiat money, or exchange-traded commodities.
Stablecoins function in several ways, depending on how they are designed and the approach used to keep the price stable. Let's start with asset-backed stablecoins. Tether, backed by USD, is one of the most well-known usd-backed stablecoins. Everyone who possesses Tether has the legal right to an equal amount of Tether in USD.
As a result, the firm behind the currency must possess all of the USD pledged to coin holders, and coin holders must believe the team that they do control all of the requisite assets. This kind of coin works quite simple. When a user buys one of the coins, the firm that created it should guarantee that they control the asset needed to support the currency and maintain it stable. The corporation is expected to get USD1 for each Tether sold in this situation. When a coin is returned to the firm, it is exchanged for USD1 and then destroyed.
What Makes Stablecoins Tick?
The method for other asset-backed stablecoins is similar: the firm behind the currency must demonstrate that they hold enough of the risky-asset to cover the number of coins released. When coins are purchased, they must produce more and buy more of the investment. They must burn the coins and compensate the client if they sell them. Users must trust a third party while using stablecoins, which isn't always desired. Some stablecoins are backed by bitcoin. Because everything is done on the blockchain and performed through smart contracts, there is no need to trust a third party (trustlessness). The problem with crypto collateralised stablecoins is that you have to give considerably more collateral than the coin is worth to account for cryptocurrency volatility.
Non-asset-backed stablecoins are much more complicated. These coins are kept to track the price of a specific item, but possessing the currency does not entitle you to the asset. These coins are managed by algorithms that continually change the total amount of cash to keep the price stable. A seigniorage shares scheme may be used to keep the price stable. As the price rises, the algorithm raises the overall supply, and when the price falls, the supply drops. Let's take a closer look at this system.
A smart contract governs the seigniorage shares mechanism. Assume this currency is attempting to maintain a steady price of USD1. If the cost exceeds USD1, the smart contract will raise the supply, selling the tokens and profiting. The profit is known as seigniorage. If the price falls below USD1, the smart contract does the inverse. The seigniorage earnings are used to repurchase a portion of the supply to raise the price.
The challenge comes when the smart contract's seigniorage earnings run out, but the price remains below USD1. In this instance, seigniorage shares must be issued and offered to purchasers with the promise of future seigniorage reimbursement. The smart contract will have enough cash after selling the seigniorage shares to boost its fixed value price to USD1. When there are no purchasers for the seigniorage shares, problems occur. If this happens, the project will collapse since the price cannot be sustained, and community sentiment will plummet substantially. As a result, this strategy is dependent on the community's continuing expansion and a rise in demand for the currency.
What Makes A Stablecoin Stable?
Some form of collateral asset backs the most successful stablecoins. You can believe that the stablecoin is worth what it should be since it can be exchanged for good collateral. As with the market factors that continuously push and pull the value of a stablecoin, these same market forces may be employed to keep stablecoin pegged. If a stablecoin begins to fall below its peak due to market oversoldness, traders (or bots) may purchase the stablecoin of the market and redeem it for the backing collateral. Purchasing the stablecoin of the market reduces its availability while increasing its value.
However, not all stablecoins are the same, and their connection to collateral might vary depending on the technique used to maintain the peg.
Government Policies
The absence of laws around stablecoins has made it simpler for issuers to make misleading claims about their support, which contributes significantly to some of them being potentially dangerous. This may change shortly, and if so, new restrictions may influence the stability and value of certain stablecoins.
Governments might establish legislation obligating stablecoin issuers to follow the same laws as banks, especially when making promises regarding reserve assets. Stablecoins may fall if issuers reject or cannot fulfill any additional regulatory criteria. Stablecoins that can meet legal criteria, on the other hand, are likely to grow safer, more generally accepted, and more efficient.
Types Of Stablecoins?
Because various assets support them, stablecoins fall into one of three categories: Stablecoins may be studied thoroughly to get a foundational understanding of the subject matter. Stablecoins may take many shapes, but they always start with the same four basic collateral structures.
In terms of the collateral structure, stablecoins fall into one of four categories:
Fiat-backed stablecoins
It is possible to create stablecoins backed by actual cash or currency equivalents. Banks worldwide issue fiat currencies like the US dollar, the British pound, and the European Union's euro. As of May 2022, Tether, Binance USD Coin (BUSD), and USD Coin are the three most popular stablecoins backed by fiat money in market capitalization (USDC).
BUSD's administrator Binance and issuer Paxos said US dollars and government debt mainly backed the stablecoin as of March 31, 2022. Circle and Coinbase have formed a collaboration called Center to create USDC, which is supported by similar assets and issued by Circle.
There is no standard method for reserving information on different currencies. It's also unclear and inconsistent how these reserves are accounted for. Tether, the largest US dollar stablecoin, has been plagued by this issue because of the ambiguity surrounding the currency's basis. Tether was penalized for unlawful reserve disclosure by multiple agencies.
Commodity-backed stablecoins
Commodity-backed stablecoins are backed by real-world assets like gold, oil, and real estate. Two of the most liquid gold-backed stablecoins are Tether Gold (XAUT) and Paxos Gold (PAXG). However, keep in mind that the value of certain assets may and will fluctuate, so you should be wary about investing in them.
Securities backed by commodities, such as stablecoins allow investors to access investments that might otherwise be out of reach. In many nations, procuring a gold bar and storing it in a secure location is difficult and expensive. As a result, physical commodities like gold and silver are not always a realistic alternative. People who want to exchange tokens for cash or gain ownership of the underlying asset may use commodity-backed stablecoins.
Stablecoin holders of Paxos Gold (PAXG) can either sell their tokens for cash or acquire the gold underpinning them. While the price of a pound of Good Delivery gold bars in London may vary between $370 and $430 per ounce, customers must have at least 430 PAXG to redeem tokens. Gold may be retrieved from vaults across the United Kingdom after token holders have stored it.
Crypto-backed stablecoins
This may seem out of place when you think about stablecoins backed by cryptocurrencies. What about the volatility of the bitcoin market, you ask? Is it possible to have stablecoins that are supported by cryptocurrencies? Crypto-collateralized stablecoins are more decentralized than stablecoins based on fiat currency. It is common for stablecoins to be overcollateralized with excessive amounts of collateral to absorb market volatility. Let's look at an example to understand the crypto-backed forms of a stablecoin further.
To get $500 worth of stablecoins, you'll need to deposit $1000 in Ether. So, you can see that stablecoins are collateralized to 200 percent, indicating a possible 25 percent decrease in price. After the price decrease, you'd still have $500 worth of stablecoins, backed by $750 worth of Ether. Stablecoins will be liquidated promptly if the value of the underlying cryptocurrency drops sufficiently.
Non-collateralized stablecoins
Non-collateralized or algorithmic stablecoins would be the fourth stablecoin category addition. Put another way, stablecoins that aren't backed by assets or collateral are called "non-collateralized." As a result, how can stablecoins with no collateral be considered stablecoins?
An algorithm controls the supply of stablecoins in non-collateralized or algorithmic forms of a stablecoin. Seigniorage shares is another name for this method. Increasing the supply of stablecoins will help restore more regular pricing for the currency. It is common to practice purchasing coins from the market to limit the amount in circulation when coin trade is meager.
Stablecoins based on algorithmic supply and demand may theoretically stabilize the market. The last point worth mentioning is the decentralization and independence provided by algorithmic stablecoins. On the other side, algorithmic blockchains depend on constant extension to succeed. Any tangible assets do not back algorithmic stablecoins. Therefore, everyone might lose money in a financial crisis.
Differences Between USDC, USDT And BUSD
Are Stablecoins Safe? - Risk Management
Although stablecoin has numerous advantages, there are a few drawbacks to be aware of. Each of them is discussed below, as well as how the difficulties might be solved.
- Counterparty risk: by relying on a third party to issue money and keep a cryptocurrency stable, some may be fractionally reserved stablecoin rather than wholly backed. In this instance, a bank deposit dip may substantially cause the coin's valuation to plummet.
- Accounts may be embezzled, banned, or accessed by unauthorized third parties if they are centralized. When a central authority can produce money without control, it faces the same monetary challenges as fiat currencies. This has the potential to cause hyperinflation.
- Manipulation of algorithms: Because most decentralized stablecoins exist behind smart contracts in protocols like Ethereum or Stellar, there is a possibility that the mechanism that maintains the money stable may fail. A third party might even influence algorithms. Because "code is law," network upgrades might impact earlier smart contracts, a significant burden for decentralized projects.
How Do Stablecoin Companies Profit?
Trading fees, interest on loans, spreads, fees from its broker programme, cloud products, interchange fees, mining services, and investment earnings are all sources of revenue for stablecoin organizations.
These companies have rapidly developed to become some of the world's top cryptocurrency exchanges in terms of the trading volume.
What Is The Most Secure Stablecoin?
USDC is often recognized as the safest stablecoin among the greatest of them all. Second, only to Tether in terms of market value, many crypto-enthusiasts have lost faith in Tether owing to its lack of transparency and history of litigation. A third-party audit of the USDC's asset reserves confirms that it was issued by members of Coinbase, a reputable organization.
As a result of the lack of a centralized issuer, some decentralization-minded cryptocurrency investors perceive Dai to be more secure than USDC in the event of an attack or collapse. Of the decentralized stablecoins, Dai is the most widely used and has the fourth-highest market value.
Finally, whatever stablecoin is best depends on how you define safety and what you want in a stablecoin.
What You Can Do With Your Stablecoins To Make Money
- Hodl: Holding your (USD) stablecoins is the most accessible approach to earning money with them if you live in a nation with a weak currency versus the US Dollar.
- Ensure Access to Liquidity: In Defi, being a liquidity provider is a simple way to make money on autopilot! By putting your money into the platform pool, you're making it more accessible to its users. As a result, you would not get gains or dividends but rather transaction fees from other customers. As a result, the more often people utilize your liquidity, the more money you earn! It goes without saying that in Defi, this is done without regard for the consequences. The smart contract on the platform is your sole ally.
- Lend: Then there's the option of lending out your stablecoins! As a result, you'd constantly receive annual percentage yields (APY). Aave and Yearn are two of the most well-known loan platforms on DeFi. Due to the decentralized nature of both CeFi and CeDeFi and their strict safety measures for DeFi investors, neither protocol has been harmed by the current market turmoil and drama like other similar protocols.
Your revenue will not be negatively impacted by the market volatility if you utilize the stablecoins that are available in the Margex wallet. Margex is notable for aggregating liquidity from different liquidity sources, fast execution of market orders, and protection features such as MP shields. Margex traders do not experience drawdowns since the aggregated order book offers traders the maximum liquidity and best available pricing for all trade pairs, leading to low spreads and decreased slippage.
- Click on "Start Trading" on Margex.com to get started trading.
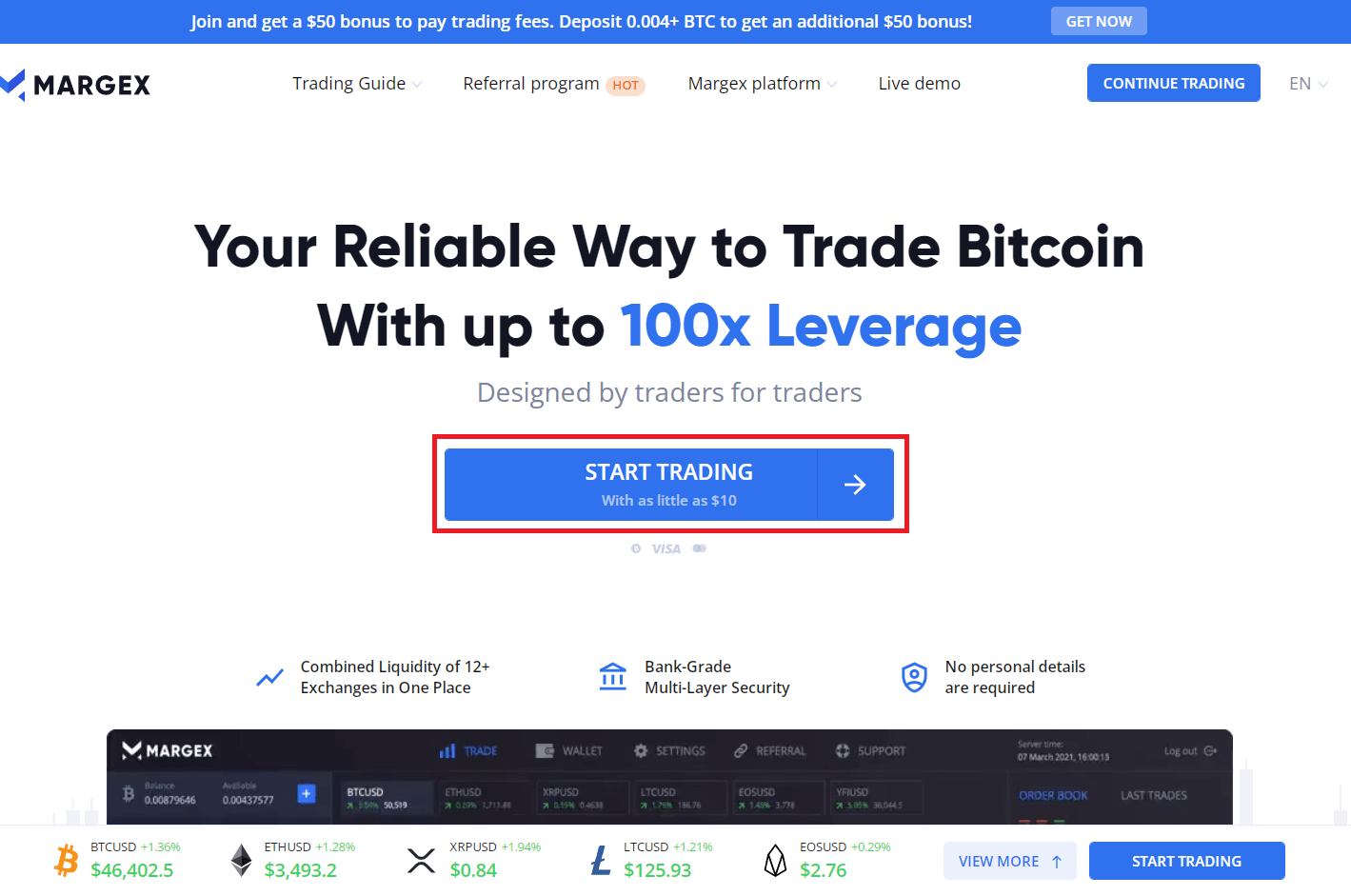
- Deposit: Click "+Deposit" on the "Wallet page." Transferring cryptocurrency to your Margex wallet or purchasing cryptocurrency using Changelly or ChangeNow are the two options for depositing funds.
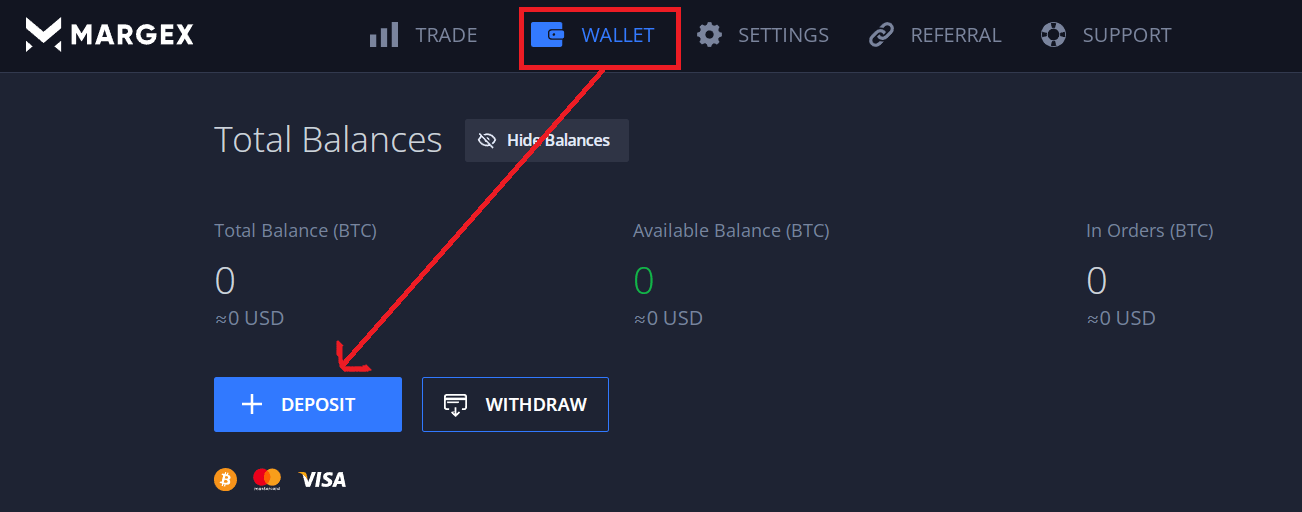
- After making a successful deposit, go to the "Trade" tab and begin trading immediately. To open a limit order, pick "Limit" as the order type and set the limit price to anything you'd like. Don't forget to select the order size, leverage, and other options.
FAQ
Is stablecoin really stable?
The most significant risk for investors wanting to invest in and retain stablecoins is volatility. Aside from volatility, it is also critical to be mindful of governance. Unlike other decentralized cryptocurrencies, a third party must control the reserve of underlying assets. As a result, the stability of stablecoins is dependent on governance and volatility.
Are stablecoins safe to hold?
Stablecoins are often considered safer than other cryptocurrencies. Typically, you don't have to be concerned about the price dropping. However, there are a few concerns to be aware of.
The first is a natural result of regular pricing. A stablecoin's price will not fall but will also not rise. By investing in stablecoins, you are foregoing the potential given by high-risk, high-reward coins. If you had invested $1,000 in Bitcoin five years ago, you would today have more than $70,000 in your account. If you had invested $1,000 in Tether five years ago, you would now have around $1,000.
Are stablecoins a good investment?
There are conflicting views on whether stablecoins are a good investment. Let's have a look at some of the reasons for and against it.
- Reasons Why Stablecoins Are a Good Investment
Investing in fiat-backed stablecoins such as USDT might be a valuable alternative for investors waiting to invest in a volatile asset such as Bitcoin. They can be converted quickly and easily and may be changed back when trust in the asset's volatility is restored.
- Reasons Stablecoins Aren't a Good Investment
As with any investment, the greater the possible benefit, the greater the risk; while certain stablecoins may gain in value over time, others may decline. This is especially true for cryptocurrency-backed stablecoins, despite the procedures to cope with the unavoidable market fluctuation.
What are the risks of staking stablecoins?
Stablecoin hazards may be comparable to those connected with conventional payment systems. They may be exposed to counterparty risk, which occurs when a third party is trusted to monitor the minting of new coins to keep the price consistent. They are also authorized to provide full collateralization. If it is discovered that this is not the case, a run on the stablecoin may occur, resulting in a significant price drop.
Can I lose money on a stablecoin?
Cryptocurrencies are used as a hedge against inflation. If your stable coin's value is tethered to USD and inflation rises, your 1 USD cryptocurrency will purchase less than previously. Stablecoins are used to protect earnings from other cryptocurrencies since other cryptocurrencies might be far more volatile and generate significant losses. Yes, there is the possibility of losing money in value. Terra Luna (UST) is a great example of a stablecoin that crashed in value..
What is the best stablecoin to use?
Among the greatest stablecoins, USDC is often considered the safest stablecoin. It is second only to Tether in terms of market capitalization, which many crypto fans no longer trust owing to its lack of transparency and history of litigation. This is not investment advice and it is advised to contact a qualified professional before investing.
Is Bitcoin a stablecoin?
No. It is a decentralized cryptocurrency based on the free market, and its value is determined by how much people are ready to pay for it. It is the inverse of stablecoins.
Is Ethereum a stablecoin?
No way. Ethereum's price, like many other cryptocurrencies, is volatile and unpredictable. Stablecoins are Ethereum-based tokens.