Because of the easy accessibility, lack of strict financial regulation, and decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies, the emerging asset class often brings many newcomers to financial markets for the first time.
The allure of life-changing ROI attracts many people who understand well the potential reward that’s possible. What these investors don’t realize is how much risk is associated with cryptocurrencies.
The risk associated with the cryptocurrency market is seemingly around every corner, and ranges from losing private keys to online scams, to sudden overreaching regulations, and of course, the notorious volatility that has become synonymous with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH).
While many of these risks you cannot escape, it is possible to reduce the risk associated with the crypto market, protect capital, and diversify a portfolio with a variety of crypto hedging strategies. To help you in your cryptocurrency trading and investing journey, we have created this beginner’s guide to hedging crypto.
What Is Hedging Crypto? A Beginner’s Guide To Crypto Hedging Strategies
When you take a position in the crypto market, your capital immediately becomes exposed to all the risks that come along with the asset class and the blockchain technology it is built on.
Hedging cryptocurrency isn’t as common investment advice as never investing more than you can comfortably afford to lose or never telling anyone how much crypto you hold, because it is a more advanced risk management strategy that takes thought and careful planning.
Common cryptocurrency hedging strategies include portfolio diversification, short-selling assets you hold, trading derivatives, crypto staking, and much more.
Why Hedge Cryptocurrency? How To Protect Capital, Lower Risk, And Increase Profits
Losses are counterproductive to capital growth. Building a well diversified portfolio can lower risk, protect capital, and increase the potential for profits.
For example, short selling can protect against capital loss by making money from a derivatives trading position if you also hold a spot position in the same underlying asset during a market downturn.
Another example involves taking a position in uncorrelated assets such as currencies or commodities. If crypto is in a downtrend and these particular assets are in an uptrend, then the ROI from winning positions can counter the losses from losing positions.
Types of Cryptocurrency Risks: What You Need To Know Before HODLing Crypto
Before we dive into crypto hedging strategies, we need to first fully understand the risks associated with the emerging digital asset class.
Volatility
Cryptocurrencies are extremely volatile compared to other asset classes. For the purpose of comparison, forex currencies typically experience 1-3% moves on an intraday basis, while cryptocurrencies can move as much as 10% to 30% in a single day. Investors can protect against unwanted drawdowns with a stop loss, while crypto traders either use short and long positions or try to sell coins at resistance and repurchase them at lower prices.
Regulation
One of the most frightening risks associated with the cryptocurrency market is the fact at any point there could be wide sweeping regulation. Many altcoins could be suddenly considered unregistered securities. Governments could ban people from owning cryptocurrencies altogether or step in in unimaginable ways. Mining could be shut down and outlawed. This dark cloud of risk is always hanging over crypto.
Hacks
Hacks are simply a part of the Internet and not necessarily cryptocurrencies alone. But because cryptocurrencies have value, they are a prime target for hackers. Hackers attack cryptocurrency exchanges, wallets, and more. In theory, any blockchain could be hacked if the hacker is skilled enough. Even 51% attacks fall under this category of risk. 51% attacks allow bad actors to gain a dominant share of a cryptocurrency’s hash power and therefore gains the power to alter the blockchain. Doing so allows hackers to reverse transactions and double spend coins.
Scams
Scams are everywhere and come in a variety of shapes and sizes. Small-time scammers could range from telling sob stories on social media and sharing a wallet address asking for donations to selling an unofficial NFT. Larger scams involve hijacking celebrity Twitter accounts to run cryptocurrency giveaway scams and smartphone SIM-swaps that give hackers access to sensitive account information so they can steal crypto assets from unsuspecting users.
Counterparty
Counterparty risk is the risk associated with another trusted party being unable to fulfill contractual obligations related to an investment. An example of this is a cryptocurrency lender being insolvent and unable to return owed customer funds. The situation is all too familiar recently, with many cryptocurrency lending firms halting withdrawals and filing for bankruptcy. Even banks themselves are only required to hold a small portion of customer funds. The rest gets reinvested by the bank for profits. Emerging cryptocurrency technologies like DeFi seek to alleviate some of this counterparty risk by keeping transactions on-chain and under the guidance of a strict decentralized computer protocol, but even DeFi isn’t entirely risk-free.
Leverage
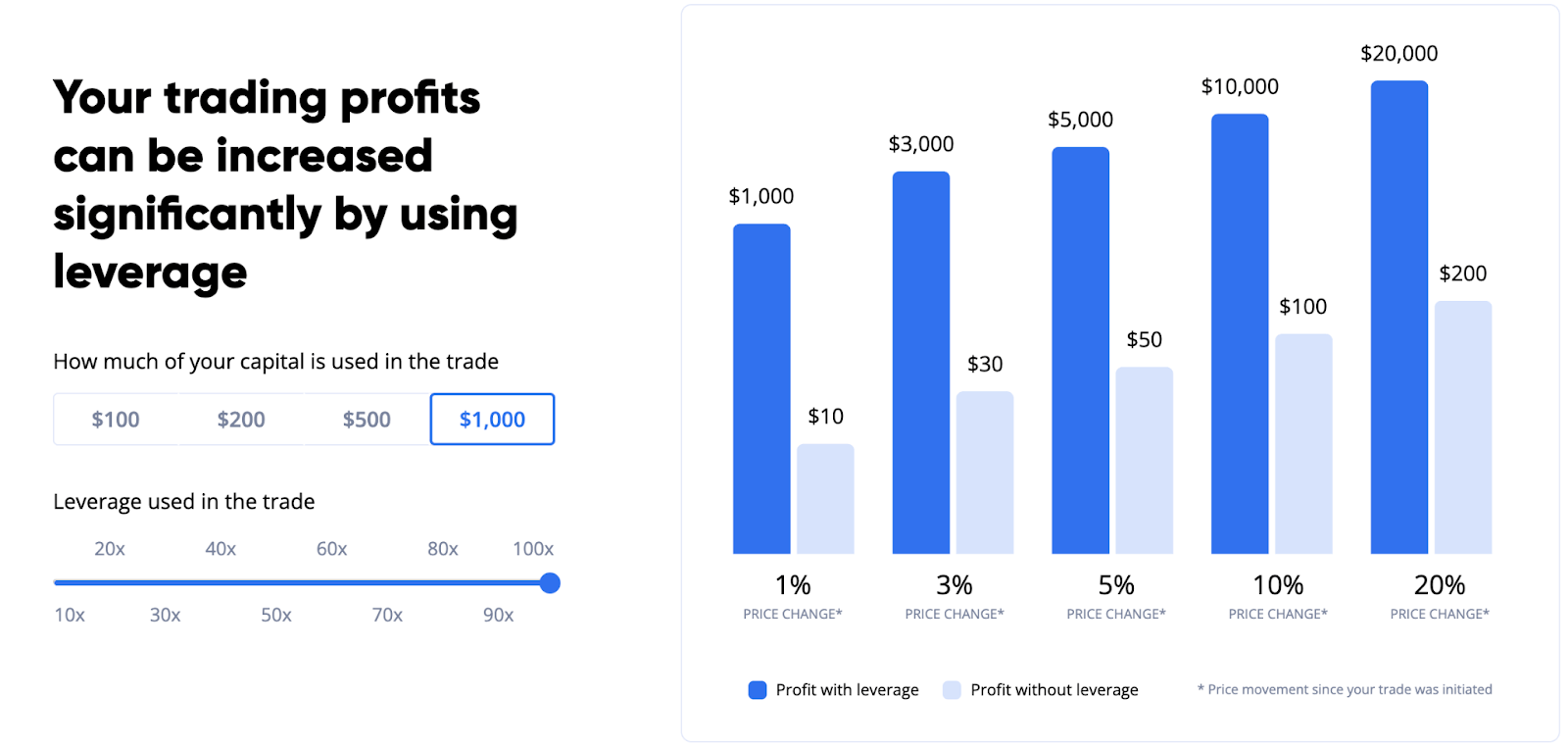
Leverage risk is in reference to a powerful derivatives trading tool offered by margin trading platforms like Margex. Leverage greatly amplifies the size of a position compared to what capital levels would normally allow. Profits are significantly increased but risk increases also. Leverage risk can be mitigated using stop-loss protection tools and preparing a trading strategy in advance with technical analysis.
How To Hedge Cryptocurrency: Common Crypto Hedging Strategies Explained
Now that you understand the risks associated with crypto and why hedging is so important to capital protection, let’s move along to the most common hedging strategies in crypto and across the greater finance space.
Short-Selling
Shorting is the number one most popular cryptocurrency hedging strategy and one of the least complicated methods on our list. It involves placing a short-sell order at key trend turning points, resistance levels, or following a confirmed breakdown from a chart pattern support.
In a short position, a trader borrows a coin and sells it when the position is opened. When the trader closes the position, they buy back the coin and profit from the difference. In a “short squeeze” situation, prices move up quickly due to short positions rapidly covering to avoid losses. The act of covering forced short traders to close rapidly in succession, creating a significant number of buy orders. Combined with natural buying of a breakout short squeeze can be especially powerful movements.
Crypto traders would use shorting as a hedging strategy to counter a spot position in the same cryptocurrency. Using an example of how to hedge Bitcoin, someone who holds BTC for the long-term might want to consider hedging spot positions with a short at resistance levels. If the market reverses, the short position ROI will counteract the losses from the decline in spot BTC value. This hedging strategy works for any type of cryptocurrency.

Staking Crypto
Shorting cryptocurrencies does take some skill and requires supporting technical analysis. However, staking among the fastest growing crypto hedging strategies today due to the relative ease related to it. Staking involves locking up idle crypto assets in exchange for a variable interest rate called an annual percentage yield (APY).
Consider a situation where the market moves sideways for an extended period. Profits are more challenging to come by at this time due to the lack of market direction. With staking, the crypto you hold can still make you more money. If you are holding crypto anyway, when the market is climbing your returns will compound due to most staking setups offering daily payouts in the cryptocurrency being staked. If the market is declining, your staking assets will earn an APY while everyone else is losing money.
Staking has become more popular over the last several years. Margex offers crypto staking with up to 13% APY interest pools that anyone can access with their idle crypto assets. Margex has also introduced an innovative trade while staking feature where users can utilize their staked crypto assets as account collateral for margin trading, enabling the ability to trade staked.
Portfolio Diversification
Portfolio diversification is the most complex of our cryptocurrency hedging strategies, because there are simply so many ways to approach it. For example, buying NFTs could be considered portfolio diversification. If you believe that Dogecoin is a better payment currency than Bitcoin, consider hedging Bitcoin with a position in Doge. If Ethereum continues to struggle with the total number of TPS it can process, a position in Solana could perform well.
There are seemingly endless ways to diversify a crypto portfolio with other digital assets. However, because the crypto asset class is highly correlated, portfolio diversification more commonly involves hedging crypto with traditional assets or cash. Moving into stablecoins that are pegged to the price of fiat currencies is also a wise hedging strategy during market downturns.
Assets with low correlation to crypto include currencies, commodities, and precious metals like gold and silver. Investors can use technical analysis software with scatterplots to compare two assets and get a better understanding of what type of correlation exists.
Derivatives Trading
Derivatives trading involves trading different types of contracts that utilize the price of a particular asset. Derivatives traders use a variety of methods to attempt to profit from normal price fluctuations.
These more advanced methods of hedging crypto with derivatives include perpetual swaps, options, and futures. We’ll examine these strategies in intricate detail in the following section.
Different Types of Derivatives Hedging Strategies: The Ultimate Crypto Hedging Strategy Explained
Trading derivatives like options, futures, and perpetual swaps is the ultimate crypto hedging strategy. Here is everything you need to know about each type.
Options
An options contract gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying at a specific strike price on or before a certain date. In options, there are four basic ways to take a position: buying a call option, selling a call option, buying a put option, and selling a put option. When taking an options position traders can buy or sell to open and buy or sell to close.
Buyers and sellers make a profit depending on the type of the option: put or call. Using call options, buyers expect the market price of an underlying asset to increase beyond the strike price. Sellers of call options expect that the price won’t increase past the strike price. Using put options, buyers are expecting the market price of an underlying asset will decline below the strike price, while the seller is betting it won't. Sellers of put options expect that the price won’t decrease past the strike price.
In options, the strike price is a fixed price at which the options trader can buy, or sell, the underlying asset or cryptocurrency. If the spot index price is the same as the options strike price, then there is zero intrinsic value of the contract. Index price must be above or below the strike price to be “in the money” or “out of the money”.
If an options trader is incorrect, since there is no obligation to exercise the contract, there is no substantial loss associated with the trade. In exchange for the lack of risk on the backside of the trade, options traders pay a premium to open the options contracts. Options sellers who offer options to collect a premium are also referred to as options writers while buyers of options are called options holders. Options writers are also sometimes called grantors.
Before considering options, it’s also important to have an understanding of options variables referred to as the Greeks. The Greeks are: vega, delta, gamma, theta, and rho. Vega measures a cryptocurrency’s price sensitivity related to its implied volatility during the duration of the options contract. Delta measures how an option’s price will change in response to a $1.00 change in the underlying crypto asset price. Gamma is a measure of how volatile an option’s price may be in response to changes in the underlying cryptocurrency’s price. Theta is a measure of time decay and its impact on an option the closer it gets to its expiration date. Rho measures how much the price of an option should rise or fall per one percentage point change in the interest rate.
Not only are options a way to spot hedge crypto or speculate, large firms who derive their revenue from cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin can use options as an insurance policy. For example, Bitcoin miners regularly hold BTC. Their entire business model depends on Bitcoin and business revenue performs best when Bitcoin is in a bull market. Such a business can buy a put option to generate ROI from the trade that offsets any decline in revenue. If the put option is incorrect, the Bitcoin miner’s business continues to thrive in a bull market and the only thing they lost was the price of the option premium.
Futures
By definition, futures are a financial contract to buy or sell in the future between two parties. Futures are derivative financial contracts which obligate the buyer to purchase an asset or the seller to sell an asset at a predetermined future date and set price. Futures typically rely on a price index of the underlying asset.
Bitcoin futures and Ethereum futures have become incredibly popular as the asset class gains wider acceptance. Futures allow investors and traders to gain exposure to these crypto assets without owning the underlying asset. Futures let traders also speculate on the future price of any cryptocurrency, hence the name. Futures can be settled in cash or in the underlying asset itself.
Futures also allow investors to hedge spot positions of the same asset. Large institutional investors might strategically plan to utilize long-term capital gains tax advantages versus short-term, and don’t want to liquidate or sell a large position in downtrend or bear market. Instead, they can hedge these spot positions with a short futures position. Futures offer a number of tax benefits, in fact.
Futures are typically listed by their expiration month. Unlike options which include time decay and eventually become worthless, futures must be settled by the buyer and seller.
Perpetual Swaps
Unlike options and futures trading, perpetual swaps never expire. Since the contracts never settle, derivatives trading platforms utilize a funding rate to ensure the contract price and spot price stay relatively similar and converge regularly.
When the contract price is trading at a rate higher than spot price, the contract is trading at a premium and longs must pay shorts a funding rate. When the contract price is trading at a rate lower than spot price, the contract is trading at a discount and shorts must pay longs a funding rate.
Since the funding rate is essentially a periodic rate paid to traders for holding positions, a high funding rate could encourage more traders to go long or short, which reduces the premium or discount. Funding rate can also put pressure on one side of the market to close and can impact trends at decisive moments. In more simple terms, the funding rate helps keep the market in balance.
Perpetual swaps let traders hedge spot crypto holdings or speculate over cryptocurrency price action. The Margex margin trading platform offers perpetual swaps on Bitcoin, Ethereum, Ripple, Litecoin, and other popular cryptocurrencies. The next section will walk you through how to use the platform to hedge crypto using perpetual swaps short positions.
How To Hedge Crypto Using Margex: A Step-By-Step Guide To Crypto Hedging Strategies
Using short positions with up to 100x leverage provided by the Margex margin trading platform, anyone can trade the hedge crypto holdings during a market downturn.
Follow these four simple steps with supporting examples.
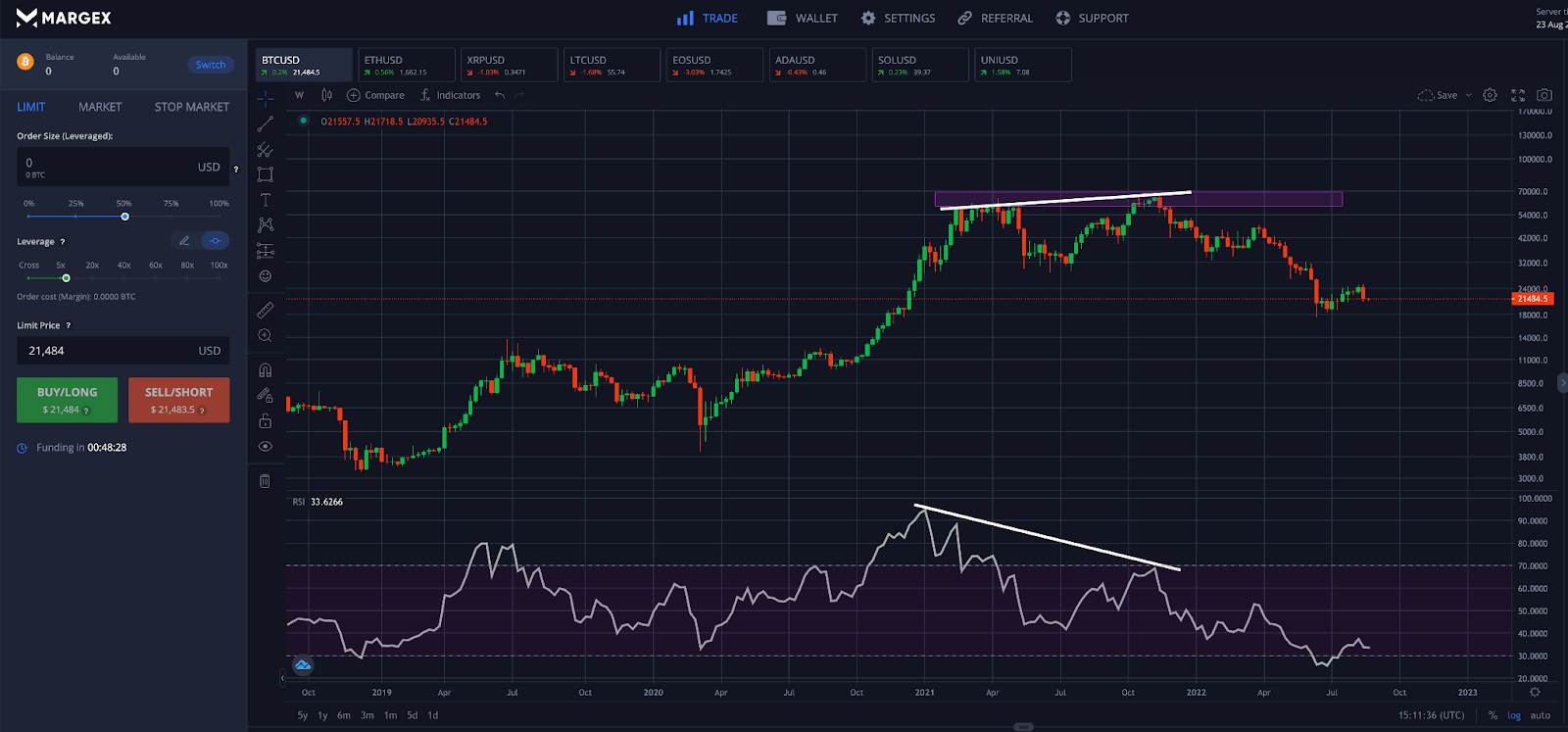
Step 1 - Open the Bitcoin (BTC) price chart, and scan the price action for resistance. Reversals commonly appear at key resistance levels and are an ideal place for a market entry.
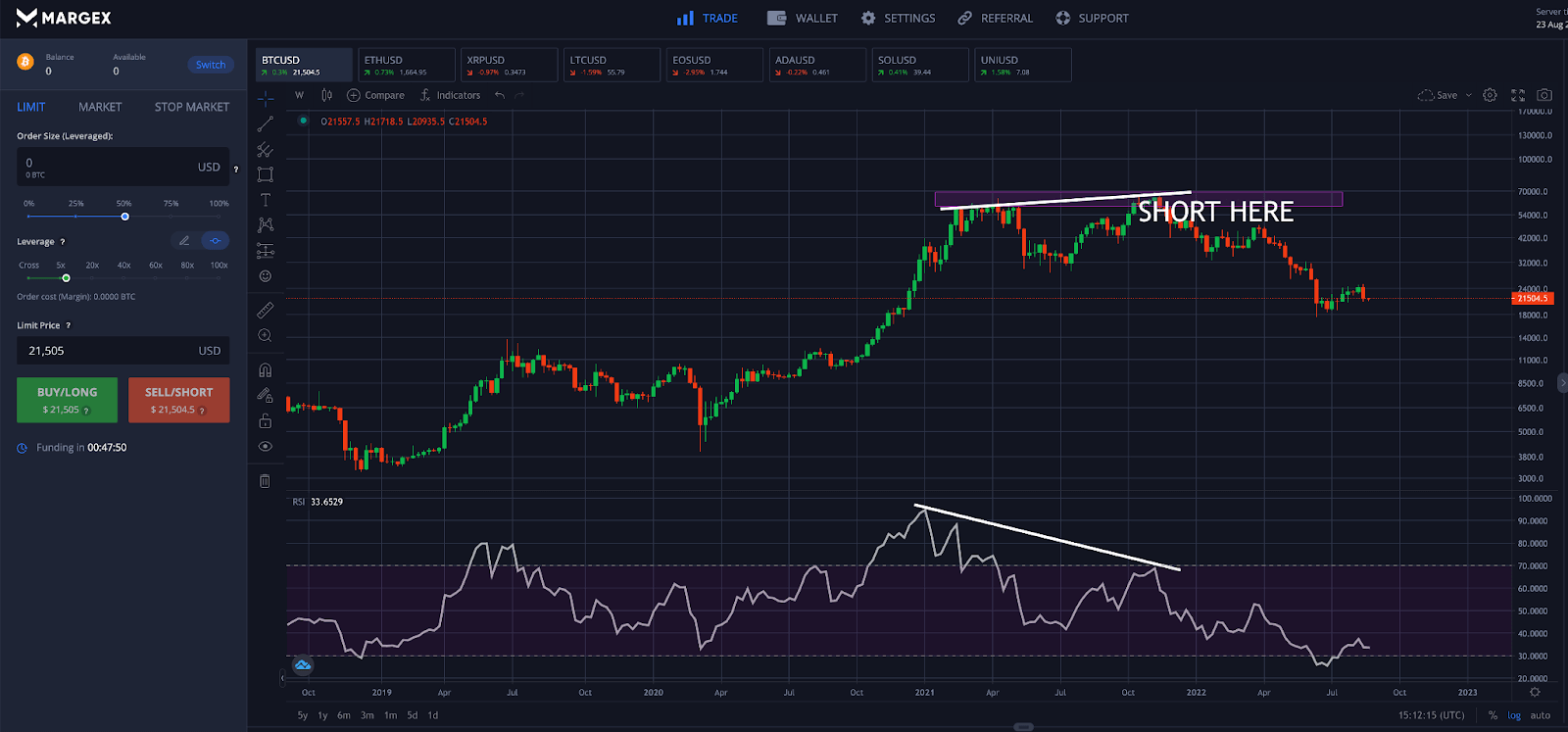
Step 2 - Look for supporting bearish signals such as doji patterns or bearish divergences. At this point, place a short-sell order to hedge your crypto holdings using perpetual swaps.
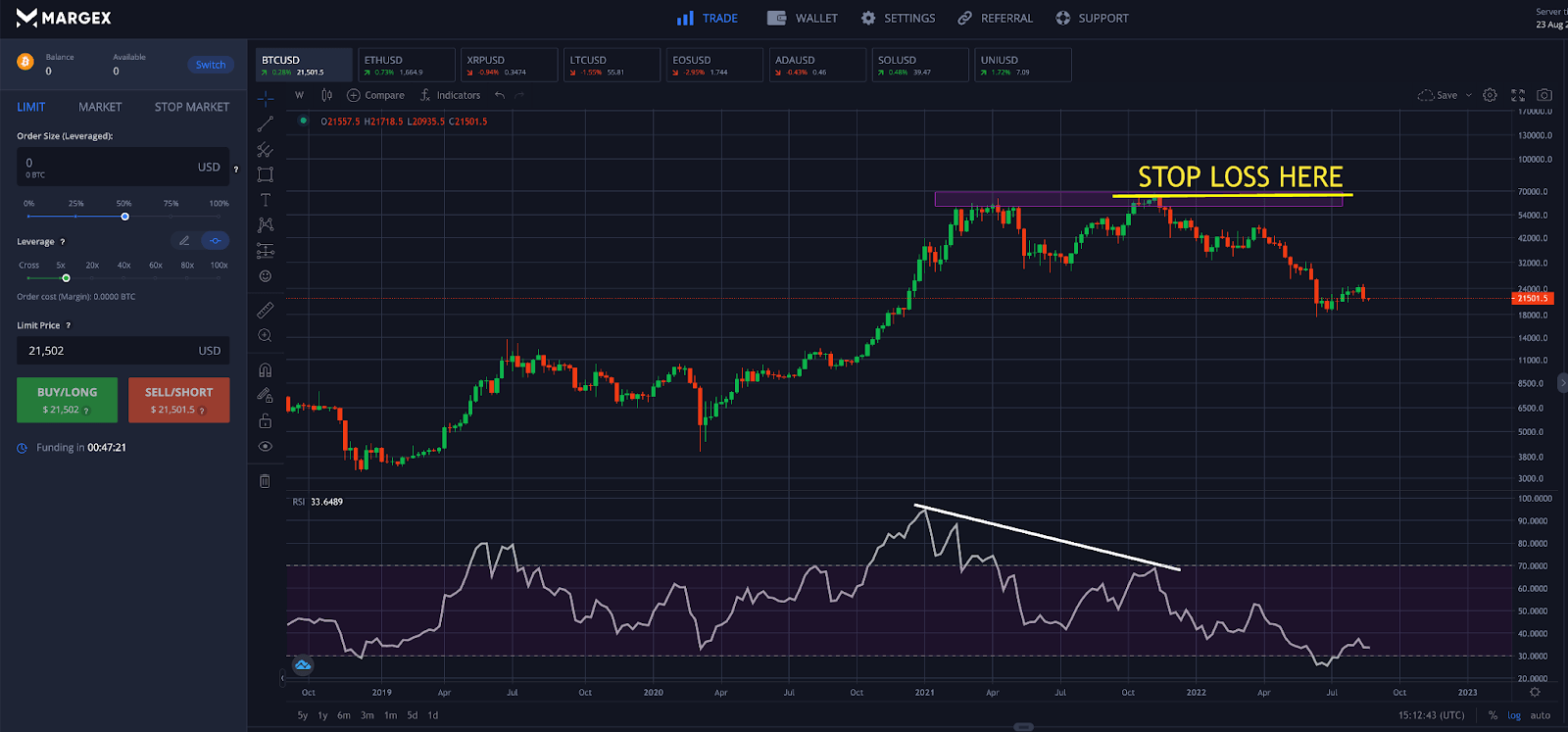
Step 3 - Place a stop loss order above the highest candle prior to the reversal. This prevents significant drawdowns from occurring if the market moves against your position.
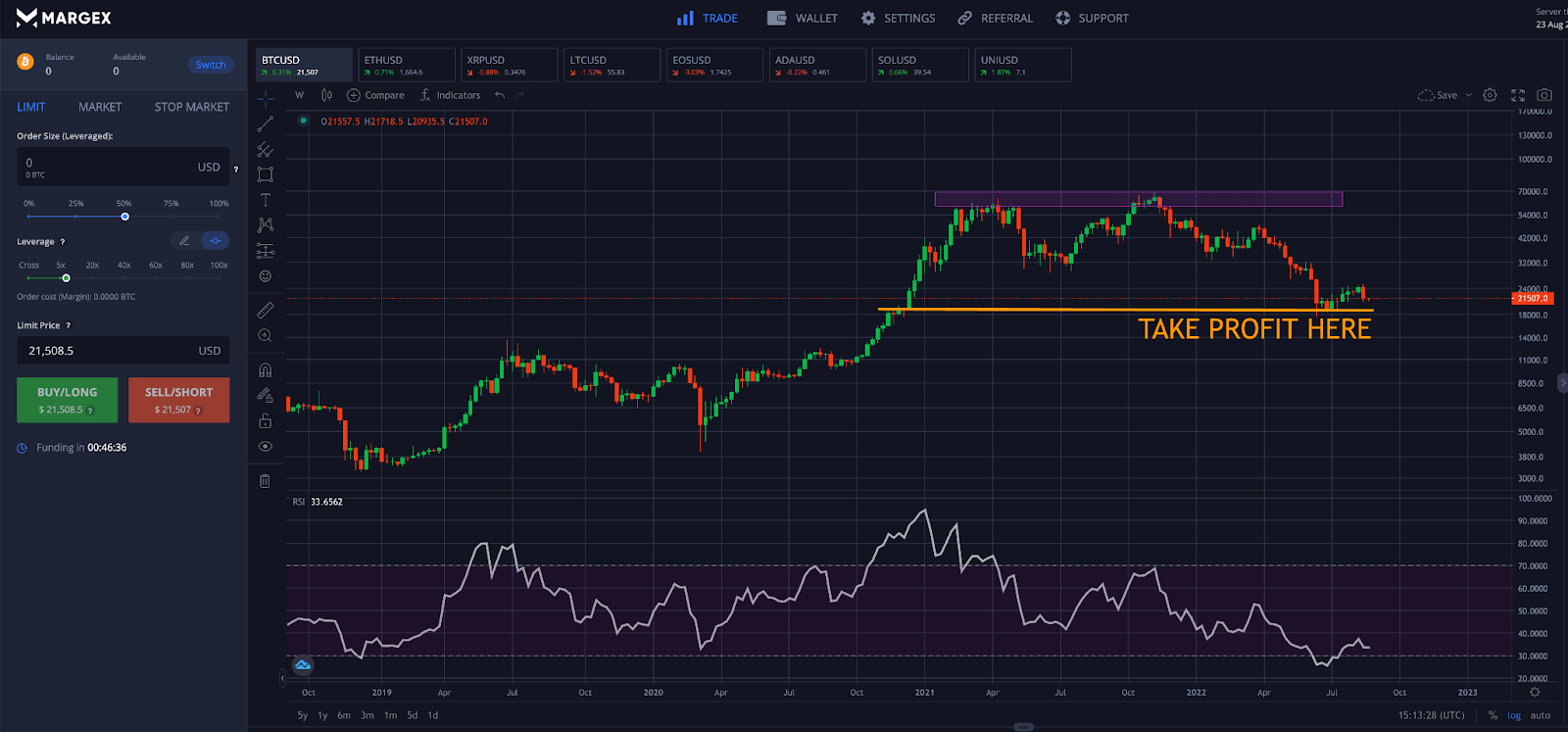
Step 4 - Plan ahead to take profit at key support levels. Congratulations, you have successfully hedged crypto!
If you don’t already have an account with Margex, sign up today with free registration and get access to world-class margin trading tools, deep liquidity, built-in charting software, and up to 13% APY staking pools.
Hedging Crypto FAQ: Commonly Asked Questions Popular Crypto Hedging Strategies
Hedging crypto is an advanced investment strategy with a wide array of ways to go about it. Due to the sheer variety and the complexity, we have prepared this list of commonly asked questions about crypto hedging strategies.
How to use crypto hedging to minimize trading risks?
There are many ways to hedge crypto effectively and use the crypto hedging strategies to protect capital against loss and increase profitability during market downturns. Oftentimes, doing so is enough to offset losses associated with declining spot asset values. Common crypto hedging strategies include staking, portfolio diversification, or derivatives trading tools like options, futures, and perpetual swaps.
How to start hedging cryptocurrencies?
Anyone can begin hedging cryptocurrencies immediately using Margex perpetual swaps. By going short Bitcoin, Ethereum, Ripple, Litecoin, and others, crypto traders and investors can hedge spot positions in crypto. Margex also offers crypto staking on idle crypto assets with an honest, up to 13% APY. For other alternatives, always do your own research and stick with trustworthy and secure platforms like Margex only.
Is hedging crypto 100% risk-free?
No crypto hedging strategy is entirely risk free, even though these concepts are designed to reduce the risks associated with cryptocurrency exposure. When using Margex perpetual swaps to hedge crypto positions, users get access to risk management tools like stop loss orders to limit unwanted losses if the market moves against the position. Risk varies across each unique crypto hedging strategy.
What is the purpose of hedging crypto?
Hedging crypto is done for the sole purpose of counteracting the risks and losses associated with cryptocurrency spot exposure. Cryptocurrencies are volatile and can lose value in an instant. While crypto spot prices are declining, a hedge short position with Margex can keep profits rolling and protect capital by offsetting losses associated with volatile crypto market drawdowns.
Is hedging a good strategy?
Hedging is a great strategy when it comes to cryptocurrencies specifically. Stock, commodities, and currencies traders all use hedge positions, why not crypto? Cryptocurrencies can decline faster than most other asset classes due to the speculative nature and strong trends related to emerging cryptocurrencies. By going short, traders can earn profit while the market is falling, helping to keep a portfolio in the green overall despite assets dropping in value.
How do you benefit from hedging?
Investors and traders can benefit from hedging in a variety of ways. For example, if hedging crypto by staking, the holder can compound returns with daily staking payouts directly to a staking balance. Going short an underlying asset you hold a spot position in can also protect capital and generate profits. Finally, portfolio diversity increases exposure to more profitable opportunities.
Is hedging possible in cryptocurrency?
Hedging is totally possible in the cryptocurrency market and you’ve come to the right place! The Margex margin trading platform has everything you need to hedge crypto, including short positions via perpetual swaps, crypto staking on idle crypto assets, and an all-new trade while staking feature where users can use staked collateral for margin trading and combined profits.
What is shorting crypto?
Shorting crypto is a hedging strategy that involves going short using perpetual swaps, options, or futures, in an asset you also hold a spot position in. Margin trading platforms offer both long and short positions with leverage so traders can profit from both directions of the market.
What is leverage in crypto?
One distinct feature of derivatives trading platforms is that leverage is offered. Leverage uses account collateral called margin to open positions at much larger sizes than what capital would normally allow. For example, buying Bitcoin at $10,000 and selling it at $60,000 would have led to a $50,000 profit. The same long trade with 100x leverage offered by the Margex margin trading platform would earn the trader $5 million in ROI. This is also why hedge short positions can keep a portfolio profitable even in a market downtrend.
What’s the difference between options, futures, and perpetual swaps?
All three are types of derivatives trading solutions that can be used to hedge crypto effectively. Options give holders the option, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a contract at a strike price before the specified date. Futures contracts the buyer and seller are required to settle the contract before the contract expiration date. Perpetual swaps have no expiration date and instead rely on a funding rate.