
As a complete beginner in the crypto world, you should understand the difference between futures trading vs. options trading. The two contracts have an expiration period in which you calculate the difference between the price at the start and end of the contract.
You can choose to pay or not to pay the premium if you go with options trading, but for futures trading, you pay for every single penny. Profits and losses might be incurred since the investor is using leveraged derivatives. In this article, you can learn more about futures trading vs. options trading.
What Are Options?
An options contract refers to trading where the contract holder has the right but is not obligated to buy (or sell) shares or assets at a particular price at any time, so long as the contract is in existence. Investors can decide whether or not to buy or sell the assets. Options trading is based on the value of the existing security.
For options, buyers are required to pay premiums to reflect 100 tokens at the asset’s strike price, the rate at which the asset should be bought or sold until the expiration date of the contract.
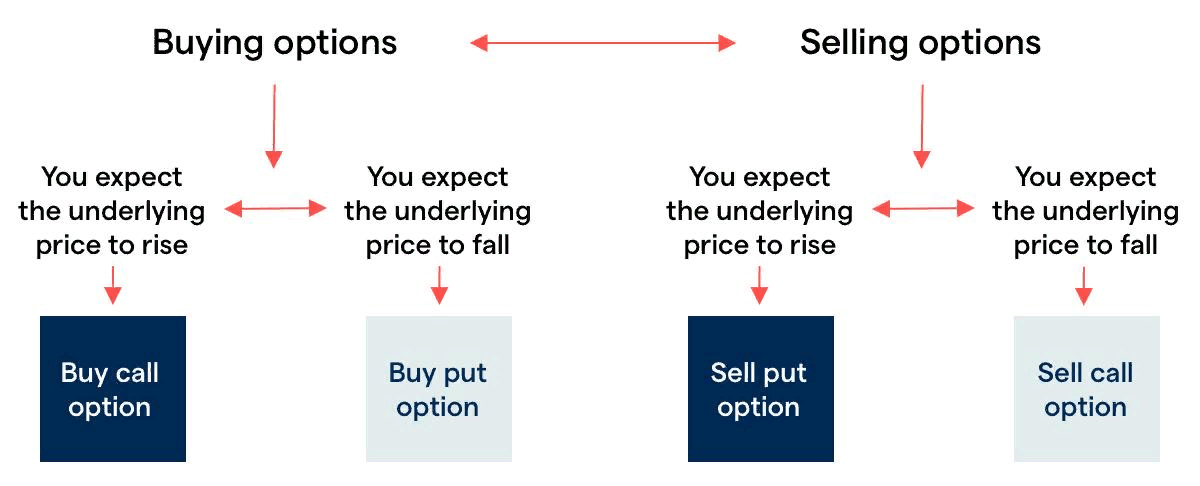
Types of Options
There are two types of options: call options and put options. A call option is an offer to buy an asset or stock at a strike price before the expiration of the agreement. For the put option, the offer is to sell the asset or stock at a particular price.
If you think the prices of the market will rise, you can opt to buy, and if you think they will fall, you can sell. Both call and put options expose you to the same level of risk. Liabilities incurred by investors are the cost of premiums paid when the contract was purchased.
Examples
Here’s an example of a call option: a contract holder opens a call option to buy asset XYZ at a $25 strike price anytime within the next two months. The stock is currently trading at $22. If the stock goes to $30, the call buyer can exercise their right to buy two shares of the stock at $50 and then sell the asset immediately for $60 to get a profit of $10.
When an investor has a put option to sell XYZ at $50, and XYZ’s price falls to $30, before the expiration of the option, the investor gains $20 for each share, less the cost of the premium. If the prices are above the $50 mark at expiration, the investor loses the premium that was paid upfront and the option is valueless.
To salvage the situation, the put buyer can close out the option position to lock the profits or losses at any time before expiration. This can be done by selling the option, or the buyer can exercise the right to sell at the strike price.
Other Possibilities
Again, the buyer can sell the call and earn the profit because the option is worth $10 per share. If the option is trading below $25 during the expiration of the contract, the option will be meaningless. At that point, the buyer will lose the upfront payment since it is used to pay for the premiums.
What are Futures?
A futures contract is a financial agreement between two parties to sell and buy an asset at a certain price in the future. future contracts, in other words, enable two parties to agree on the price at which they will trade an asset in the future. Although the length of future contracts varies, each contract’s settlement dates are always set. In other words, before two parties may enter into a crypto futures contract, they must agree on a predetermined settlement date.
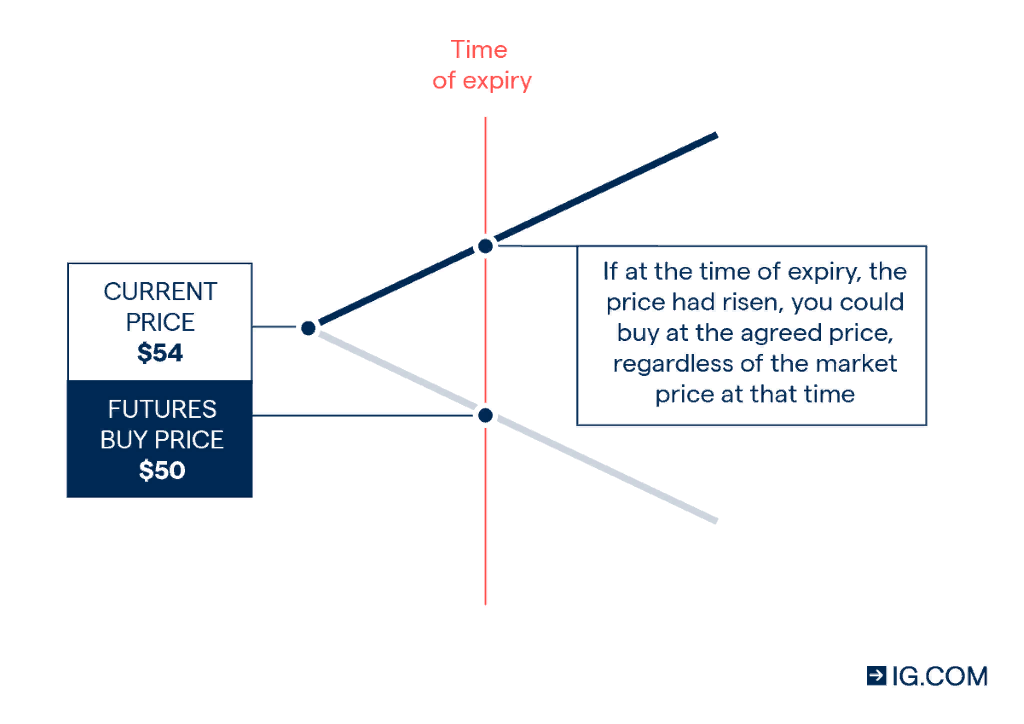
Examples
For a better understanding of futures, here’s an example: Assume the price of bitcoin is $40,000, and June, a crypto derivatives trader, believes the price will rise in a month.
She could bet on this probability by agreeing to buy 1 BTC for $40,000 a month from today. All she has to do now is open bitcoin futures contracts, which collectively signal her commitment to pay $40,000 for 1 BTC next month, independent of the spot market price.
John, on the other hand, predicts that at the scheduled settlement date, the price of bitcoin will fall below $40,000. Next month, he plans to sell June $40,000 in contracts. To put it another way, June is "longing" bitcoin and John is "shorting" it.
If the price of bitcoin rose to $45,000 by the contract’s expiration date, June would have made a $5,000 profit because she got BTC at a discount from John. In the event that the price of BTC fell below $40,000 on the settlement date, June would be forced to purchase bitcoin from John at a higher price than the current market, resulting in a loss.
Other Possibilities
If you want to buy gold on a futures contract, the immediate factor to be determined is how long you foresee holding the contract. When purchasing futures, you agree to buy the asset at the price indicated in the contract. Say gold is currently trading at $1,800 and the contract matures in June of next year. No matter what happens within that period, the amount you must pay will be constant.
Perpetual Swaps
A perpetual swap contract is the most popular futures contract in crypto. It is in a way similar to a futures contract. You can say it’s the upgraded version of a futures contract. Perpetual swaps vary from traditional futures contracts in that they do not have an expiration date. In essence, this eliminates the need to re-establish a long or short position on a regular basis. As a result, perpetual contracts’ pricing must be tied to the spot prices of their underlying assets. The value of the contract and the underlying asset automatically converge as the expiration date approaches in the case of futures, thus there is no need to maintain a price peg.
Because perpetual swaps have no expiration dates, exchanges use a price anchoring approach called the funding rate mechanism. By encouraging or disincentivizing trades, this mechanism balances the short and long positions of perpetual swaps. Consider it a discount or price that serves to balance the demand for both short and long-term perpetual contracts.
The Key Difference Between Futures and Options
Both options and futures are financial instruments that are used to make profits or hedge against the movement of prices of commodities or investments. The key difference lies in the freedom the contract holder has. For futures contracts, the contract holder is required to buy the underlying asset on a specified date in the future, while for options, the contract holder has an option to decide whether they will carry out the contract.

This difference affects how investors can use financial instruments to make money. Also, it determines how futures and options are traded and priced.
Is Futures Trading the Same as Options?
Future trading is not the same as options trading because when trading with futures, the contract holder can purchase a specific asset and the seller can sell and deliver that asset at a particular future date unless the holder’s position is closed before expiration. On the other hand, in options trading, the holder has a right but is not obligated to sell or buy an underlying asset at a specific price during the life of the contract.
On the expiration date, you as the contract holder are required to settle the difference between the contract’s opening and closing price. For futures, you must pay your trades in full, while for options, you may choose whether or not to pay the premium.
Is It More Profitable to Trade Options or Futures?
The profitability of the two financial instruments depends on the factors the investor is interested in. A futures contract is less volatile when it comes to changes in prices, and can fall below $0, while with options, the price fluctuates more with changes in the asset’s value. Also, prices cannot go below $0.
Which is Riskier, Futures or Options
Trading options can be riskier than futures because they are more complex. The two types of options, call and put, bear the same level of risk. When an investor opts to buy a stock on options, the liability is the cost of the premium at the time it was purchased.
However, a futures contract usually involves big leverage. If the markets go against you, your position has a chance of getting liquidated – in other words, you’ll lose the whole amount of your invested funds (margin).
What Should I Choose for Trading?
If you’re a trader who is at a crossroads and is confused about whether to trade with futures or options, perpetual swaps might be the solution for you.
If you trade on options the benefits are, trading with leverage, trading for a longer time, and getting access to the platform 24/7. You can also find weekly or quarterly contracts and enjoy limited risk.
When trading on a perpetual account for a futures contract you enjoy the same benefits as options and you’re more likely to hedge against volatility.
The downside of the two contracts is that you are trying to predict the future and you can either make profits or losses.
Factors to Consider Before Choosing
There are several factors a trader ought to consider before choosing the way to go. How long do you want the contract to last, and what kind of risk are you willing to deal with? When you use financial derivatives, it is easier to predict whether there will be a rise or fall in the price of the asset in question.
If you have all the necessary information, you can buy or sell depending on whether the price rises or falls. This gives you room to escape the uncertainties that come with futures contracts.
Conclusion
Both futures and options are worth giving a try. They both have an advantage against the other, and the decision lies with the trader. Before choosing either futures or options, you must know the main goal you want to achieve. If it is a long-term goal in terms of investment, the futures option is the way to go; if it is short-term, go with options. And in case you would like to trade crypto derivatives, Margex is one of the BEST exchanges offering x100 leverage on your trades.
Either of these contracts (or both) can be a promising way to invest your money, just be sure to understand how they work and remember about the risks involved.
FAQ
What is the difference between options and futures?
Futures are contracts that give the holder the right to buy or sell a specific asset at a predetermined price on a specific date in the future. Options provide the right to purchase or sell a certain asset at a specific price on a specific date, but not the duty to do so.
Can you make more money in futures or options?
Both options and futures have limitless profit possibilities. While futures trading has a basic linear reward — a trader makes money when the price moves in their favor and loses money when the price moves against them — So options are more complicated and therefore suitable for professional traders only. Most crypto platforms don’t offer them because of this.
Which is riskier, futures or options?
There is no simple answer to this question. While options are risky and complicated, futures can be even riskier for individual investors.


