
Market liquidity refers to how easily assets can be quickly bought or sold in a market without causing significant price changes. It is a key factor in market efficiency, influencing how smoothly transactions occur. High liquidity means that assets can be traded swiftly with minimal price impact, fostering market stability and boosting investor confidence.
Conversely, low liquidity can lead to unpredictable price fluctuations and increase risks for market participants. This concept is particularly relevant in the fast-changing cryptocurrency markets, where liquidity levels can greatly affect investment strategies and market outlooks.
Impact of Liquidity on Cryptocurrency Markets
The distributed character of cryptocurrencies, worldwide and around-the-clock trading, and a broad spectrum of players define their markets. They run constantly, unlike conventional markets, which might have more liquidity prospects.
Still, liquidity on various cryptocurrencies and trading sites might fluctuate greatly. Major cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum usually display better liquidity because of their great acceptance and the many exchanges supporting them, which enable quick transactions with little price slippage.
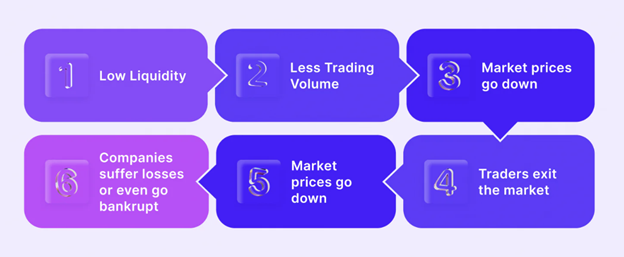
Trading volume and the network effect— wherein a rising number of users buying, selling, and trading a coin improves liquidity—impact liquidity. This impact is especially noticeable in cryptocurrencies that enable several uses, including smart contracts and distributed apps (dapps), drawing a large user and developer base.
Furthermore, the possibility of liquidity fragmentation among several exchanges, which would affect trading conditions and possible arbitrage opportunities, is noteworthy.
Key Factors Affecting Liquidity in Cryptocurrency Markets
Several interconnected factors impact the liquidity of cryptocurrency markets:
Market Sentiment: Liquidity depends much on public opinion and investor confidence. Positive news or developments can draw more people, improving liquidity; bad events could cause less participation, affecting liquidity.
Trading Volume: Higher trade volumes suggest a market with plenty of buyers and sellers, indicating liquidity immediately.
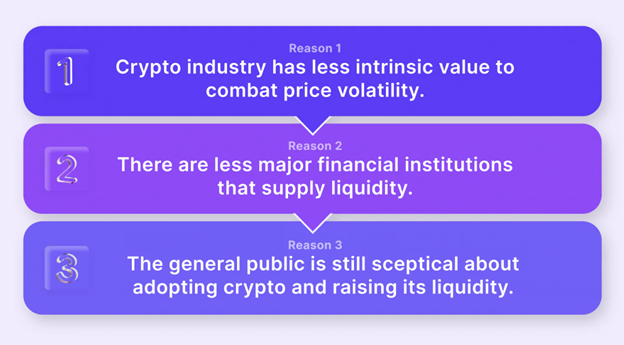
Regulation: Favorable and clear regulations can boost investor confidence and market participation, thereby improving liquidity.
Technological Advancements: Innovations that enhance transaction efficiency, security, and user experience can attract a more extensive user base and increase liquidity.
Adoption and Integration: Integrating cryptocurrencies into the broader financial ecosystem can broaden their user base and improve liquidity.
Managing Liquidity on Cryptocurrency Exchanges
To manage liquidity, cryptocurrency exchanges especially distributed ones, often employ Automated Market Makers (AMMs). Unlike conventional order book models, AMMs present a different trading and liquidity management method.
Here’s how AMMs manage liquidity on these exchanges:
1.Liquidity Pools
AMMs use smart contracts and liquidity pools, including several token reserves. Direct token exchanges between traders against these pools will replace conventional buyers and sellers, removing their requirements. Algorithms oversee all trading operations housed in these pools.
2.Pricing Mechanism
The ratio of tokens determines token prices within liquidity pools. This ratio changes with each trade, affecting the token prices. Initially, AMMs used the constant product formula: x × y = k, where x and y represent the quantities of two tokens and k is a constant. This formula ensures that total liquidity remains stable after trades. Many AMMs have since developed variations of this formula, such as Uniswap V3 and V4, Balancer, and Curve.
3.Liquidity Providers
Users who contribute tokens to liquidity pools are known as liquidity providers (LPs). They receive liquidity tokens representing their pool share and earn some transaction fees from trading activities. These fees help compensate LPs for the risk of impermanent loss.
4.Impermanent Loss
Impermanent loss occurs when the value of tokens in a liquidity pool changes relative to their value when deposited. The greater the price change, the higher the potential loss compared to holding the tokens outside the pool. Some AMMs offer strategies to mitigate this loss, such as insurance mechanisms or adjusted fee structures.
5.Governance and Upgrades
Governance tokens are often used in AMMs to vote on protocol changes, including fee adjustments and updates to liquidity pool algorithms. This decentralized governance allows AMMs to adapt quickly to new tokens and evolving pricing mechanisms.
6.Integration With Other Protocols
Often integrating with other distributed finance (DeFi) systems, AMMs improve their capabilities. They might, for instance, engage with lending systems to apply borrowed money to create liquidity. This connection adds to today’s more complicated and linked financial ecosystem.
By providing distributed, effective, and adaptable solutions for liquidity management, AMMs have revolutionized trade by lowering entrance barriers for liquidity providers and increasing access to financial services inside the crypto realm.
What Occurs During a Liquidity Crisis?
Theoretical effects of liquidity levels have been covered in the past parts. Actually, liquidity crises are more frequent than predicted and impact both conventional trading markets and cryptocurrencies. The American housing bubble of 2008 is clearly illustrates a liquidity crisis.
At first, one could naturally believe that a crisis limited to one market or nation would not have worldwide effects. Still, the consequences of the US housing crisis are felt everywhere even after fifteen years.
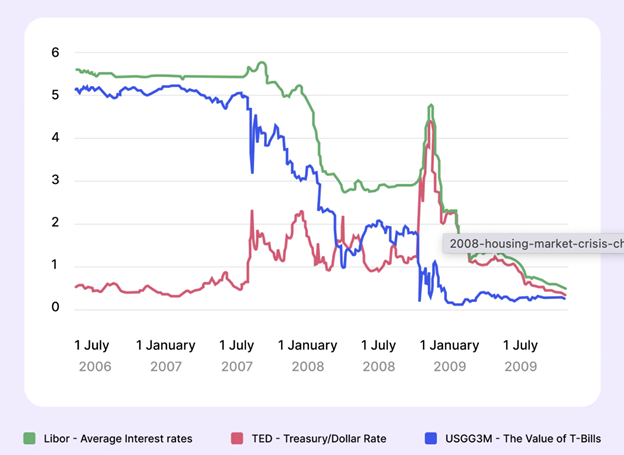
A legislative reform in the US financial industry allowing banks to offer collateralized debt obligations to the general public set off this major collapse. It was clear by 2008 that these high-risk investments were fast turning into liabilities.
Understanding Liquidity’s Influence on Cryptocurrency Trading
In cryptocurrency markets, liquidity shapes trade speed and price stability. Understanding how liquidity affects trading can help create sensible plans for various market situations. This overview provides an understanding of methods fit for both low- and high-liquidity situations and shows how liquidity influences traders.
Price Impact and Slippage
High Liquidity: When there is a lot of money in the market, traders can make big deals that don’t change the object’s price much. This leads to low slippage, which means that the price of execution is very close to the price that was predicted.
Low Liquidity: Low liquidity, on the other hand, can cause big changes in prices even for small trades. This makes trading more expensive because the execution price is farther from the expected price. This is called bigger slippage.
Trade Execution Speed
High Liquidity: In highly liquid markets, orders are carried out faster since there are many players and enough assets to satisfy buy and sell orders.
Low Liquidity: Trade in less liquid markets may suffer delays. Less participation and restricted resources mean that orders may not be filled at the intended price or remain unmet.
Market Volatility
High Liquidity: In high-liquidity marketplaces, many buyers and sellers usually help to stabilize prices, so individual deals find it more challenging to produce appreciable price movements. This usually yields lower trading expenses and narrower bid-ask spreads.
Low Liquidity: Conversely, low liquidity markets are more prone to show noticeable price movements, which little trades or news events could set off. The larger bid-ask spreads in such markets raise trading expenses since buying and selling prices vary greatly.r.
Strategies for Trading in Different Liquidity Conditions
Strategies for Low Liquidity Markets
Limit orders help traders specify precise purchase or selling prices, reducing slippage and safeguarding against negative price fluctuations.
Position Sizing: Reducing trade amounts can control slippage and aid in limiting market impact.
Avoid Market Orders: Low liquidity conditions could lead to less desired prices, so they are perfect for avoiding market orders.
Optimal Timing: Trading at busy times or when significant markets intersect will help to boost liquidity and execution quality.
Strategies for High-Liquidity Markets
Scalping: By making frequent, rapid trades, traders can profit from the narrow spreads of high-liquidity markets by taking advantage of small price fluctuations.
Algorithmic Trading: Using the liquid market environment, algorithms can run quick trades to profit on small price variations.
High-frequency trading (HFT): This strategy uses great liquidity for quick returns. It entails making many fast trades to benefit from few price fluctuations.
Market Orders: Orders are efficient for instantaneous execution at the best available pricing in high liquidity conditions.
Maximizing efficiency and controlling risks depend on changing trading methods depending on liquidity situations. In either high or low liquidity conditions, the objective is to reduce risks while taking advantage of possibilities from both scenarios.
Challenges Affecting Liquidity in Cryptocurrency Markets
Key Liquidity Issues
Cryptocurrency markets encounter several challenges that impact liquidity, including:
High Volatility: Crypto markets’ inherent volatility can lead to rapid and unpredictable price changes, which can affect the stability and availability of liquidity.
Regulatory Uncertainties: Inconsistent or unclear regulatory frameworks can create uncertainty, potentially deterring market participants and reducing liquidity.
Technological Constraints: Limitations in current technology can hinder efficient trading and settlement processes, impacting overall market liquidity.
Efforts to Improve Liquidity
To tackle these challenges, various initiatives are being pursued:
Market Infrastructure Enhancement: Efforts are focused on improving the underlying infrastructure to support better market functioning and depth.
Efficient Trading Systems: The development of more efficient trading and payment systems aims to facilitate smoother transactions and enhance liquidity.
Balanced Regulatory Frameworks: Establishing regulatory frameworks that both protect investors and encourage market growth is crucial for fostering a more stable liquidity environment.
Innovative Solutions
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Protocols: Liquidity can be improved creatively using deFi protocols and liquidity pools. These systems let participants offer liquidity in return for incentives, hence strengthening and deepening the market.
Automated Market Makers (AMMs): By automating market-making techniques, AMMs have changed liquidity provision. This helps to sustain ongoing market liquidity and lessens reliance on conventional buyers and sellers.
These approaches represent significant advancements in addressing liquidity challenges and improving overall market stability.
Future Outlook How Liquidity is Impacting Cryptocurrency Markets
Driven by continuous innovations in distributed finance (DeFi), changing legal frameworks, and technical advancement, the view of liquidity in the crypto markets is progressively bright. Liquidity levels will increase as the market changes and institutional investors become more engaged.
Solutions for interoperability and cross-chain technology are ready to address market fragmentation, possibly producing a more liquid and united market. These developments will likely support more market stability and efficiency as cryptocurrencies are becoming increasingly adopted worldwide.


